USG of Kidney
Protocols
Normal Kidney Usg Measures :
Anatomy of kidney:
1.Length: 11 cm (9-12 cm)
2.Width: 5 cm
3.Anero-posterior diameter: 2.5 cm
4.Parenchymal thickness = 1-2.5 cm
5.Cortical thickness: Should be more than 1cm.
6. children, Length of kidney should be = 6 + 1/3rd of age
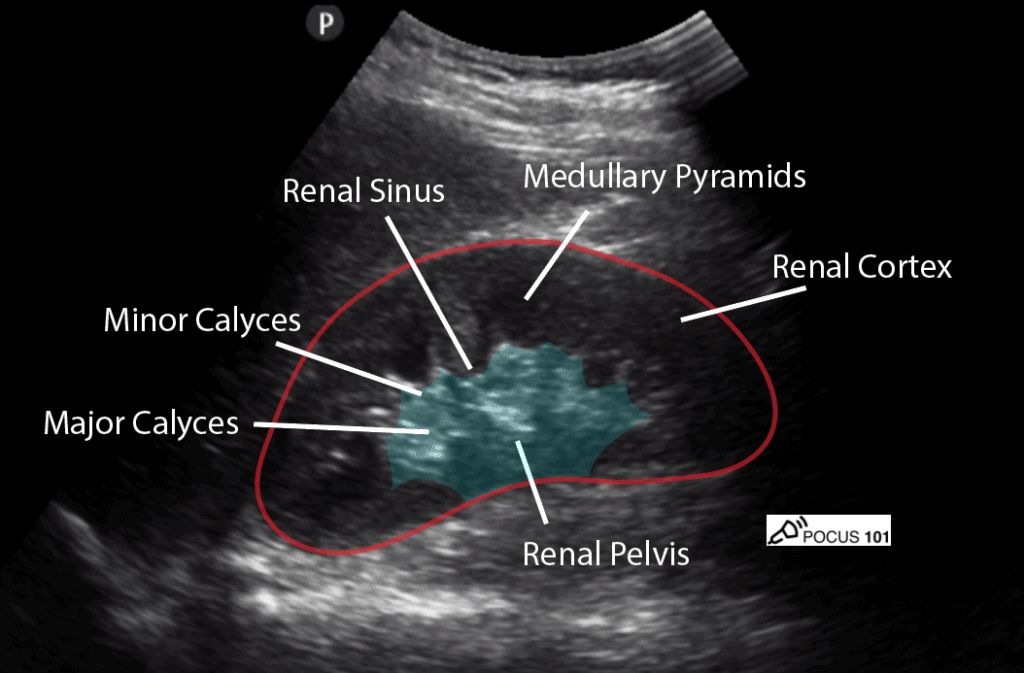
🌏Kidney USG Ecogenicity :
1.Cortex ➡️ Hypoechoic than liver
2.Medulla ➡️ More hypoechoic than cortex
3.Renal Sinus ➡️ Echogenic as it contains fat
USG findings of polycycystic kidney disease :

1.On imaging, it usually presents on ultrasound with enlarged echogenic kidneys with multiple small cysts.
2. Liver involvement with coarse echotexture, biliary tract cystic changes, and portal hypertension may be evident, depending on the age and stage of hepatic fibrosis.
USG of Acute Pyelonephritis:

1.Diffuse or focal enlargement of the kidney.
2.variation in parenchymal echogenicity (usually hyperechoic).
4.loss of corticomedullary differentiation, decreased visualization of renal sinus fat.
Chronic Pyelonephritis usg findings :

1.The typical radiologic findings of chronic pyelonephritis are focal scars in the polar regions of the kidney with calyceal distortion.
2. pelvicalyceal dilatation, and global atrophy caused by reduced growth of the kidney due to chronic disease;
3. compensatory hypertrophy of contralateral kidney is common.
Hydronephrosis usg findings :
1.grade 0
no dilatation, calyceal walls are apposed to each other.
2.grade 1 (mild)
dilatation of the renal pelvis without dilatation of the calyces (can also occur in the extrarenal pelvis)
no parenchymal atrophy
3.grade 2 (mild)
dilatation of the renal pelvis (mild) and calyces (pelvicalyceal pattern is retained)
no parenchymal atrophy
4.grade 3 (moderate)
moderate dilatation of the renal pelvis and calyces
blunting of fornices and flattening of papillae
mild cortical thinning may be seen
5.grade 4 (severe)
gross dilatation of the renal pelvis and calyces, which appear ballooned
loss of borders between the renal pelvis and calyces
renal atrophy seen as cortical thinning.
Kidney stone USG:

1.echogenic foci.
2.acoustic shadowing.
3. twinkle artefact on color Doppler.
4.color comet-tail artefact.
CKD USG findings :

1.reduced renal cortical thickness
2.reduced renal length.
3.increased renal cortical echogenicity.
4.poor visibility of the renal pyramids and the renal sinus.
5.marginal irregularities.
6.papillary calcifications.
Cystitis USG(UB inflammation):
1.wall thickening and irregularity with intraluminal filling defects, caused by blood clots.
2.In late stages, the bladder may become fibrotic and have a small volume. Irregular bladder wall calcification may develop.